Instantaneous acceleration, meanwhile, is the limit of the average acceleration over an infinitesimal interval of time. In the terms of calculus, instantaneous acceleration is the derivative of the velocity vector with respect to time:
Uniform circular motion. 9-29-99 Sections 5.1 – 5.2 Uniform circular motion. When an object is experiencing uniform circular motion, it is traveling in a …
The solution of the problem about the catenary was published in \(1691\) by Christiaan Huygens, Gottfried Leibniz, and Johann Bernoulli.. Below we derive the equation of catenary and some its variations.

Description of Rotation. Rotation is described in terms of angular displacement , time , angular velocity, and angular acceleration . Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement and angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity.
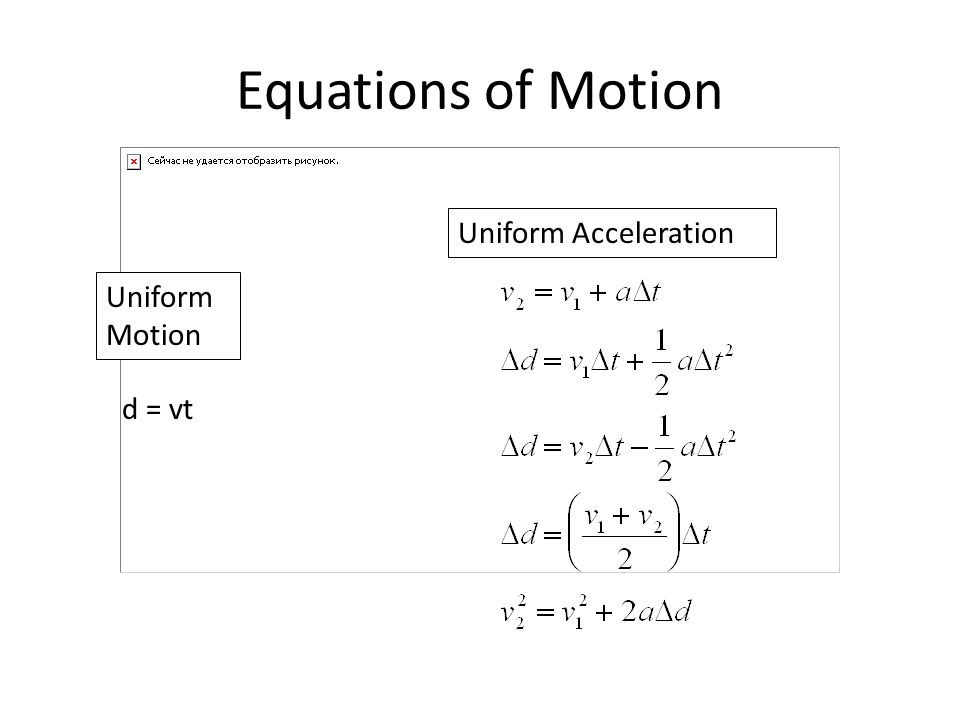
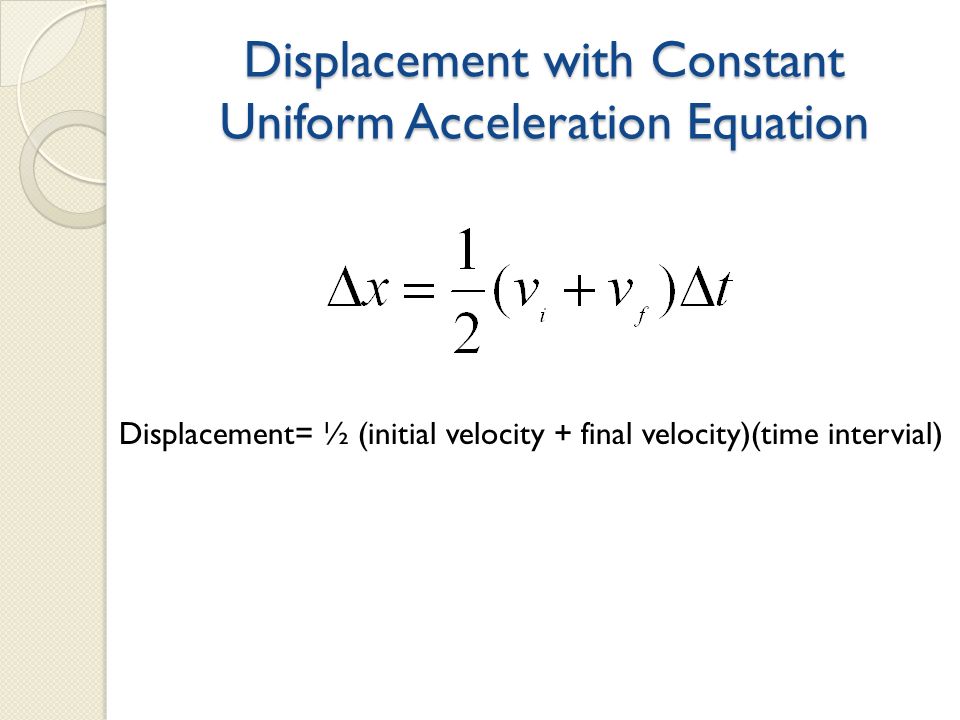
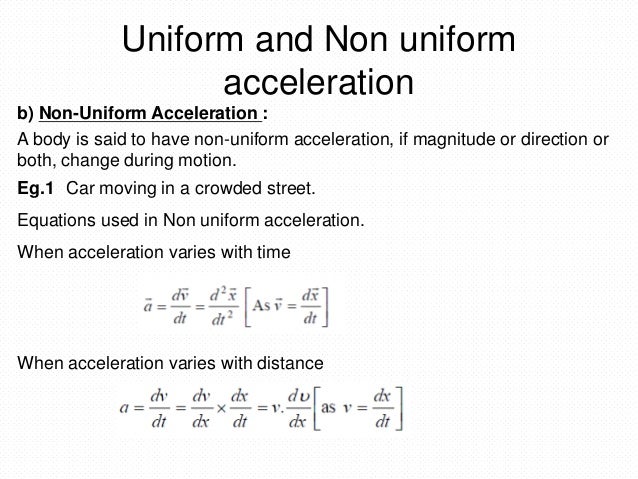
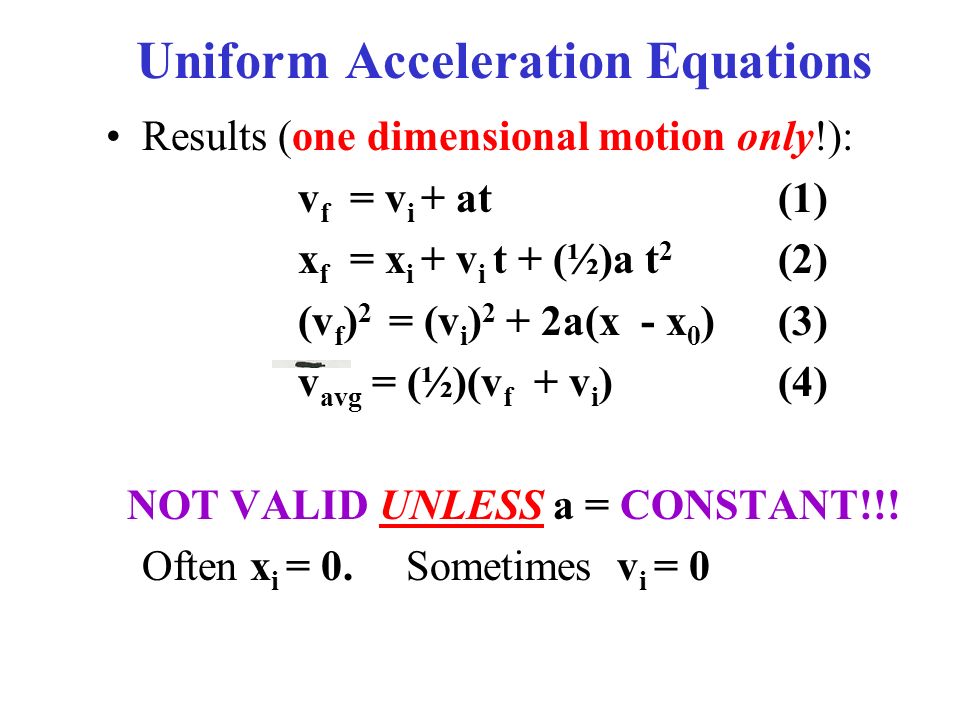
In mathematical physics, equations of motion are equations that describe the behaviour of a physical system in terms of its motion as a function of time. More specifically, the equations of motion describe the behaviour of a physical system as a set of mathematical functions in terms of dynamic variables: normally spatial coordinates …

Biomechanics is the science concerned with the internal and external forces acting on the human body and the effects produced by these forces
The acceleration which is gained by an object because of the gravitational force is called its acceleration due to gravity.Its SI unit is m/s 2.Acceleration due to gravity is a vector, which means it has both a magnitude and a direction.
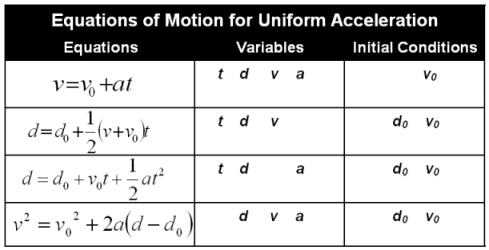
Essay Writing Service in Australia – Aussiessay.com acceleration = (change in velocity) ÷ time.. Acceleration is a vector when it refers to the rate of change of velocity. . Acceleration is scalar when it refers to rate of change of sp
Speed and Velocity Acceleration The Centripetal Force Requirement The Forbidden F-Word Mathematics of Circular Motion There are three mathematical quantities that will be of primary interest to us as we analyze the motion of objects in circles. These three quantities are speed, acceleration and

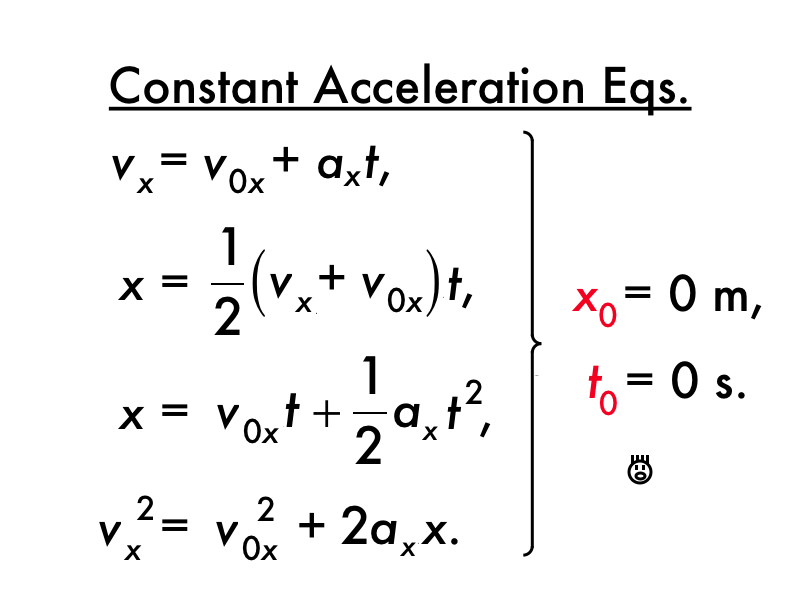

The final mathematical quantity discussed in Lesson 1 is acceleration. An often confused quantity, acceleration has a meaning much different than the meaning associated with it by sports announcers and other individuals.
